PROJECTS CENTER

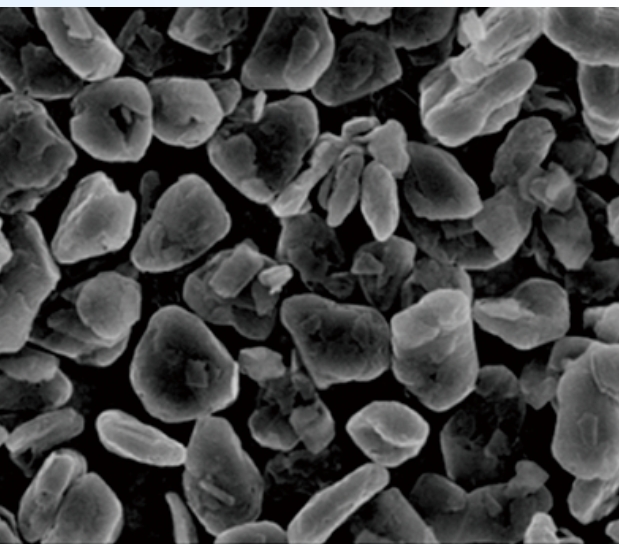
Natural Graphite Anode Material
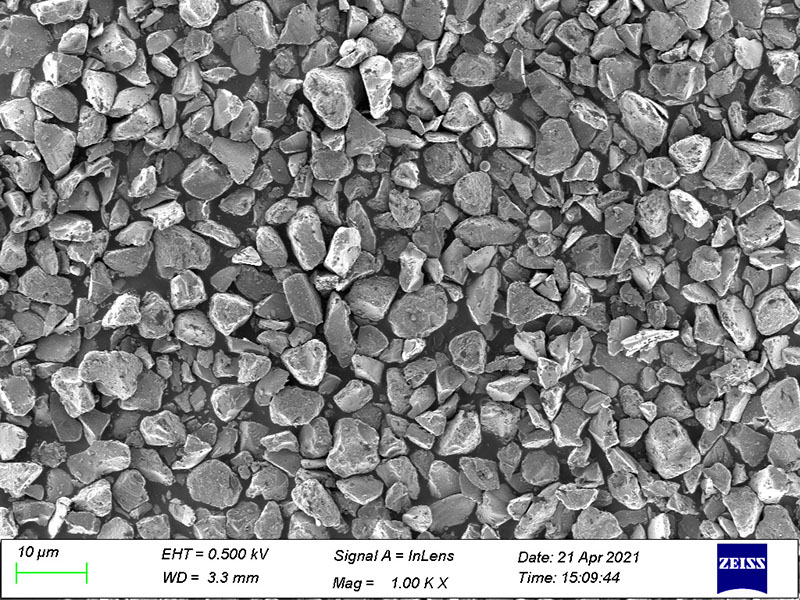
Natural graphite, a carbon-based mineral with a layered hexagonal crystal structure, is a widely used anode material due to its high theoretical capacity (~372 mAh/g), low cost, and abundant reserves.
The indirect co-precipitation method involves first preparing a transition metal salt solution with a stoichiometric ratio, then adding a precipitating agent to obtain a ternary mixed co-precipitation precursor.
The indirect co-precipitation method involves first preparing a transition metal salt solution with a stoichiometric ratio, then adding a precipitating agent to obtain a ternary mixed co-precipitation precursor.
Silicon-carbon anode materials are composed of nano-scale silicon particles (Si, 20-200nm) compounded with carbon matrices (graphite/CNTs/graphene).
Silicon monoxide anode materials are primarily composed of silicon monoxide compounded with carbon materials.
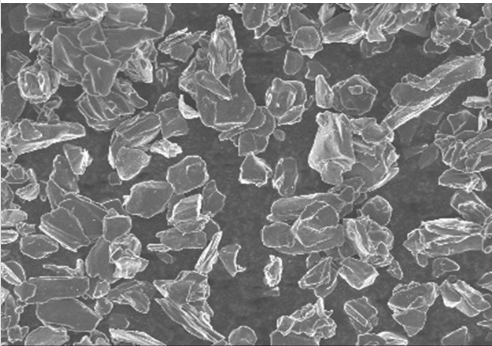
Artificial Graphite Anode Materials
Artificial graphite is a high-performance carbon material widely used as the anode in lithium-ion batteries (LIBs). It is synthesized from carbonaceous precursors like petroleum coke, pitch coke, or coal tar pitch through processes including crushing, graphitization (heat treatment at 2800–3000°C), and surface modification.